最近在学习PKI,顺便接触了一些加密算法。对RSA着重研究了一下,自己也写了一个简单的实现RSA算法的Demo,包括公、私钥生成,加解密的实现。虽然比较简单,但是也大概囊括了RSA加解密的核心思想与流程。这里写下来与大家分享一下。
RSA概述:
RSA是目前最有影响力的公钥加密算法,它能够抵抗到目前为止已知的绝大多数密码攻击,已被ISO推荐为公钥。 RSA的数学基础是大整数因子分解问题,其说明如下:
-
给定两个素数p、q,计算乘积pq=n很容易
-
给定整数n,求n的素因数p、q使得n=pq十分困难
RSA的密码体制:
设n=pq,其中p和q是大素数。设P=E=Zn,且定义K={(n,p,q,a,b):ab≡1(modΦ(n)) }其中 Φ(n)=(p-1)(q-1)。对于K={(n,p,q,a,b)} 定义加密 E(x)=xb mod n; 解密D(y)=ya mod n;(x,y∈Zn),值n,b组成了公钥,p、q和a组成了私钥
- RSA生成秘钥步骤
- 随机生成两个大素数p、q,并计算他们的乘积n
- 计算k=(p-1)(q-1)
- 生成一个小于k且与k互质的数b,一般可使用65537
- 通过求出a关于k的反模a。
代码如下:
首先,写出三个封装类,PrivateKey.java PublicKey.java RsaKeyPair.java (JDK中的实现高度抽象,这里我们就简单的封装一下)

1 package com.khalid.pki; 2 3 import java.math.BigInteger; 4 5 public class PublicKey { 6 7 private final BigInteger n; 8 9 private final BigInteger b; 10 11 public PublicKey(BigInteger n,BigInteger b){ 12 this.n=n; 13 this.b=b; 14 } 15 16 public BigInteger getN() { 17 return n; 18 } 19 20 public BigInteger getB() { 21 return b; 22 } 23 } 
1 package com.khalid.pki; 2 3 import java.math.BigInteger; 4 5 public class PrivateKey { 6 7 private final BigInteger n; 8 9 private final BigInteger a; 10 11 public PrivateKey(BigInteger n,BigInteger a){ 12 this.n=n; 13 this.a=a; 14 } 15 16 public BigInteger getN() { 17 return n; 18 } 19 20 public BigInteger getA() { 21 return a; 22 } 23 } 
1 package com.khalid.pki; 2 3 public class RsaKeyPair { 4 5 private final PrivateKey privateKey; 6 7 private final PublicKey publicKey; 8 9 public RsaKeyPair(PublicKey publicKey,PrivateKey privateKey){ 10 this.privateKey=privateKey; 11 this.publicKey=publicKey; 12 } 13 14 public PrivateKey getPrivateKey() { 15 return privateKey; 16 } 17 18 public PublicKey getPublicKey() { 19 return publicKey; 20 } 21 }
生成大素数的方法没有自己实现,借用了BigInteger类中的probablePrime(int bitlength,SecureRandom random)方法
SecureRandom random=new SecureRandom();random.setSeed(new Date().getTime());BigInteger bigPrimep,bigPrimeq;while(!(bigPrimep=BigInteger.probablePrime(bitlength,random)).isProbablePrime(1)){ continue; }//生成大素数p while(!(bigPrimeq=BigInteger.probablePrime(bitlength,random)).isProbablePrime(1)){ continue; }//生成大素数q
计算k、n、b的值
1 BigInteger n=bigPrimep.multiply(bigPrimeq);//生成n2 //生成k 3 BigInteger k=bigPrimep.subtract(BigInteger.ONE).multiply(bigPrimeq.subtract(BigInteger.ONE)); 4 //生成一个比k小的b,或者使用65537 5 BigInteger b=BigInteger.probablePrime(bitlength-1, random);
核心计算a的值,扩展欧几里得算法如下
注意第二个方法 cal 其实还可以传递第三个参数,模的值,但是我们这里省略了这个参数,因为在RSA中模是1
1 private static BigInteger x; //存储临时的位置变量x,y 用于递归 2 3 private static BigInteger y; 4 5 6 //欧几里得扩展算法 7 public static BigInteger ex_gcd(BigInteger a,BigInteger b){ 8 if(b.intValue()==0){ 9 x=new BigInteger("1"); 10 y=new BigInteger("0"); 11 return a; 12 } 13 BigInteger ans=ex_gcd(b,a.mod(b)); 14 BigInteger temp=x; 15 x=y; 16 y=temp.subtract(a.divide(b).multiply(y)); 17 return ans; 18 19 } 20 21 //求反模 22 public static BigInteger cal(BigInteger a,BigInteger k){ 23 BigInteger gcd=ex_gcd(a,k); 24 if(BigInteger.ONE.mod(gcd).intValue()!=0){ 25 return new BigInteger("-1"); 26 } 27 //由于我们只求乘法逆元 所以这里使用BigInteger.One,实际中如果需要更灵活可以多传递一个参数,表示模的值来代替这里 28 x=x.multiply(BigInteger.ONE.divide(gcd)); 29 k=k.abs(); 30 BigInteger ans=x.mod(k); 31 if(ans.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO)<0) ans=ans.add(k); 32 return ans; 33 34 } 我们在生成中只需要
1 BigInteger a=cal(b,k);
就可以在Log级别的时间内计算出a的值
将以上代码结合包装成的 RSAGeneratorKey.java

1 package com.khalid.pki; 2 3 import java.math.BigInteger; 4 import java.security.SecureRandom; 5 import java.util.Date; 6 7 public class RSAGeneratorKey { 8 9 private static BigInteger x; //存储临时的位置变量x,y 用于递归 10 11 private static BigInteger y; 12 13 14 //欧几里得扩展算法 15 public static BigInteger ex_gcd(BigInteger a,BigInteger b){ 16 if(b.intValue()==0){ 17 x=new BigInteger("1"); 18 y=new BigInteger("0"); 19 return a; 20 } 21 BigInteger ans=ex_gcd(b,a.mod(b)); 22 BigInteger temp=x; 23 x=y; 24 y=temp.subtract(a.divide(b).multiply(y)); 25 return ans; 26 27 } 28 29 //求反模 30 public static BigInteger cal(BigInteger a,BigInteger k){ 31 BigInteger gcd=ex_gcd(a,k); 32 if(BigInteger.ONE.mod(gcd).intValue()!=0){ 33 return new BigInteger("-1"); 34 } 35 //由于我们只求乘法逆元 所以这里使用BigInteger.One,实际中如果需要更灵活可以多传递一个参数,表示模的值来代替这里 36 x=x.multiply(BigInteger.ONE.divide(gcd)); 37 k=k.abs(); 38 BigInteger ans=x.mod(k); 39 if(ans.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO)<0) ans=ans.add(k); 40 return ans; 41 42 } 43 44 public static RsaKeyPair generatorKey(int bitlength){ 45 SecureRandom random=new SecureRandom(); 46 random.setSeed(new Date().getTime()); 47 BigInteger bigPrimep,bigPrimeq; 48 while(!(bigPrimep=BigInteger.probablePrime(bitlength, random)).isProbablePrime(1)){ 49 continue; 50 }//生成大素数p 51 52 while(!(bigPrimeq=BigInteger.probablePrime(bitlength, random)).isProbablePrime(1)){ 53 continue; 54 }//生成大素数q 55 56 BigInteger n=bigPrimep.multiply(bigPrimeq);//生成n 57 //生成k 58 BigInteger k=bigPrimep.subtract(BigInteger.ONE).multiply(bigPrimeq.subtract(BigInteger.ONE)); 59 //生成一个比k小的b,或者使用65537 60 BigInteger b=BigInteger.probablePrime(bitlength-1, random); 61 //根据扩展欧几里得算法生成b 62 BigInteger a=cal(b,k); 63 //存储入 公钥与私钥中 64 PrivateKey privateKey=new PrivateKey(n, a); 65 PublicKey publicKey=new PublicKey(n, b); 66 67 //生成秘钥对 返回密钥对 68 return new RsaKeyPair(publicKey, privateKey); 69 } 70 }
编写一个简单的JUnit测试代码,没有把结果以字节流编码显示 ,比较懒。。。。

1 package com.khalid.pki; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 5 public class RSATest { 6 7 @Test 8 public void testGeneratorKey(){ 9 RsaKeyPair keyPair=RSAGeneratorKey.generatorKey(256); 10 System.out.println("n的值是:"+keyPair.getPublicKey().getN()); 11 System.out.println("公钥b:"+keyPair.getPublicKey().getB()); 12 System.out.println("私钥a:"+keyPair.getPrivateKey().getA()); 13 } 14 15 16 }
这样秘钥对的生成工作就完成了
加密与解密
加密与解密的根本就是使用E(x)=xb mod n D(y)=ya mod n这两个公式,所以我们首先要将数据转化为最底层的二进制串,在转换为BigInteger进行计算,将结果做成Base64码
代码如下

1 package com.khalid.pki; 2 3 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 4 import java.math.BigInteger; 5 import java.util.Arrays; 6 7 import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64; 8 9 public class RSAUtil { 10 11 public static String encrypt(String source,PublicKey key,String charset){ 12 byte[] sourceByte = null; 13 try { 14 sourceByte = source.getBytes(charset); 15 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 BigInteger temp=new BigInteger(1,sourceByte); 20 BigInteger encrypted=temp.modPow(key.getB(), key.getN()); 21 return Base64.encodeBase64String(encrypted.toByteArray()); 22 } 23 24 public static String decrypt(String cryptdata,PrivateKey key,String charset) throws UnsupportedEncodingException{ 25 byte[] byteTmp=Base64.decodeBase64(cryptdata); 26 BigInteger cryptedBig=new BigInteger(byteTmp); 27 byte[] cryptedData=cryptedBig.modPow(key.getA(), key.getN()).toByteArray(); 28 cryptedData=Arrays.copyOfRange(cryptedData, 1, cryptedData.length);//去除符号位的字节 29 return new String(cryptedData,charset); 30 31 } 32 } 很坑爹的一点是要记得BigInteger是有符号位的。重组String时要记得去除符号位,不然中文的时候会莫名其妙在第一位多出空格。
在编写一个测试代码就Ok了

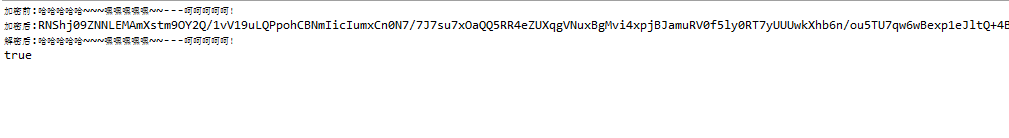
1 package com.khalid.pki; 2 3 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 6 public class RSATest { 7 8 9 @Test 10 public void testRSA() throws UnsupportedEncodingException{ 11 //生成KeyPair 12 RsaKeyPair keyPair=RSAGeneratorKey.generatorKey(1024); 13 // 元数据 14 String source = new String("哈哈哈哈哈~~~嘿嘿嘿嘿嘿~~---呵呵呵呵呵!"); 15 16 System.out.println("加密前:"+source); 17 //使用公钥加密 18 String cryptdata=RSAUtil.encrypt(source, keyPair.getPublicKey(),"UTF-8"); 19 System.out.println("加密后:"+cryptdata); 20 //使用私钥解密 21 try { 22 String result=RSAUtil.decrypt(cryptdata, keyPair.getPrivateKey(),"UTF-8"); 23 System.out.println("解密后:"+result); 24 System.out.println(result.equals(source)); 25 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 26 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 } 31 } 测试结果。bingo。